Treatment of Gum Diseases
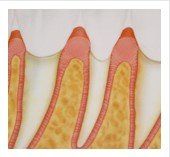
Gingivitis & Periodontitis
Gum disease, is the process that begins when bacterial growth in your mouth begins to lead to the corrosion of your teeth and gums. If left untreated, long-term effects include extensive gum deterioration, along with early tooth loss.
There are two stages in gum disease of which include: gingivitis (gum inflammation) followed by periodontitis (gum disease). Within the stages of gingivitis, the bacteria in hardened plaque pockets build up causing the gums to become irritated and swell. When brushing your gums may appear red or may bleed easily. Despite gum irritation, the roots of your teeth are still firmly in their place.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis. During this process, the gums begin to pull away from the tooth creating pockets where bacteria can collect and spread. Toxins produced by the bacteria, along with enzymes present in your body’s natural defense of infections, begin to eat at the bone and tissue that anchor your tooth. As the process continues, the corrosion spreads and more gum tissue and bone are damaged. When this happens, teeth are no longer anchored in place, thus resulting in permanent tooth loss.
While tartar buildup is the leading cause of gum disease, there are additional contributing factors. Some of these include: illnesses that affect the immune system (HIV, diabetes), poor lifestyle habits such as smoking or a diet high in sugar, poor oral hygiene habits or a family history of periodontal disease.
Some symptoms of gum disease include:
- Gums that are susceptible to bleeding
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- A receding gum line
- Loose or shifting teeth
Some progression of gum disease may be present in your gums despite not having any symptoms. This is a reason why regular dental check ups are important in the prevention and treatment of gum disease. Only a dentist or periodontist will be able to recognize symptoms of gum disease.
If you live in or around [city] and you suspect you may be in need of gum disease treatment or if you have any questions, contact us or fill out an appointment request form today to schedule a consultation with one of our periodontists. Our specialists are experts in evaluating your oral health and will advise you along the appropriate treatment process.